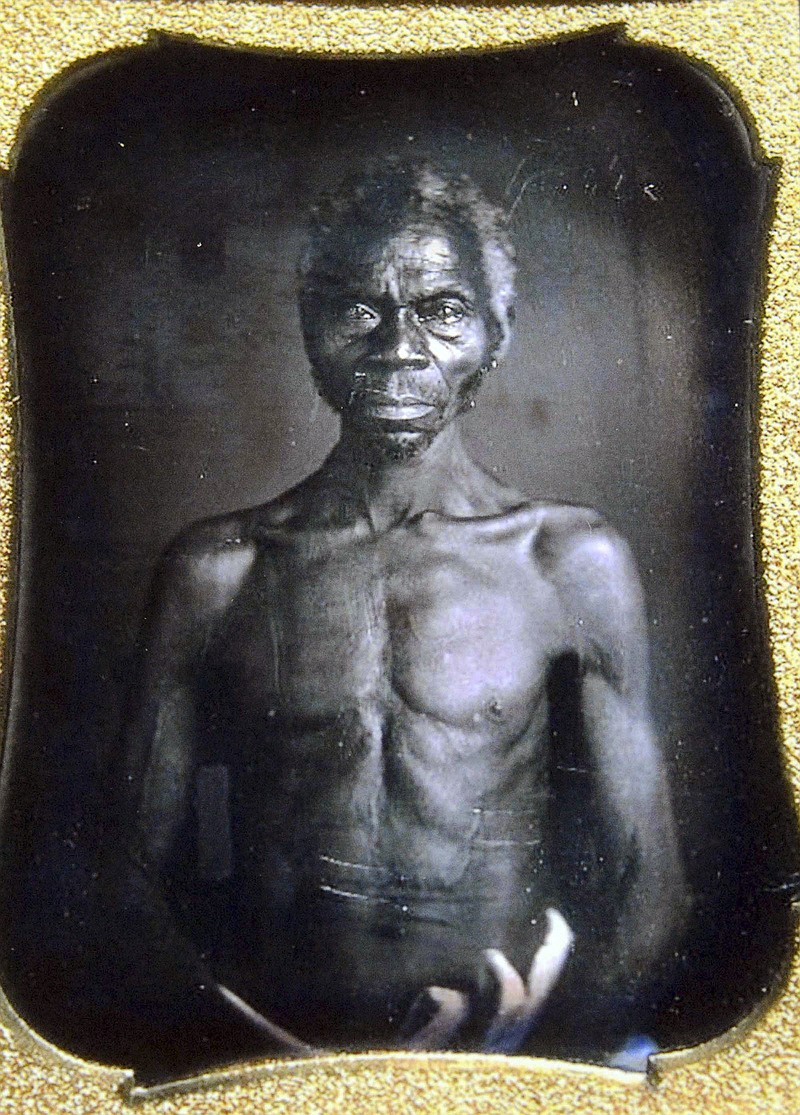
BOSTON (AP) — Harvard University has “shamelessly” turned a profit from photos of two 19th-century slaves while ignoring requests to turn the photos over to the slaves’ descendants, according to a lawsuit filed Wednesday.
Tamara Lanier, of Norwich, Connecticut, is suing the Ivy League school for “wrongful seizure, possession and expropriation” of images she said depict two of her ancestors. Her suit, filed in Massachusetts state court, demands Harvard immediately turn over the photos, acknowledge her ancestry and pay an unspecified sum in damages.
Harvard spokesman Jonathan Swain said the university “has not yet been served, and with that is in no position to comment on this complaint.”
At the center of the case is a series of 1850 daguerreotypes, an early type of photo, taken of two South Carolina slaves identified as Renty and his daughter, Delia. Both were posed shirtless and photographed from several angles. The images are believed to be the earliest known photos of American slaves.
They were commissioned by Harvard biologist Louis Agassiz, whose theories on racial difference were used to support slavery in the U.S. The lawsuit says Agassiz came across Renty and Delia while touring plantations in search of racially “pure” slaves born in Africa.
“To Agassiz, Renty and Delia were nothing more than research specimens,” the suit says. “The violence of compelling them to participate in a degrading exercise designed to prove their own subhuman status would not have occurred to him, let alone mattered.”
The suit attacks Harvard for its “exploitation” of Renty’s image at a 2017 conference and in other uses. It says Harvard has capitalized on the photos by demanding a “hefty” licensing fee to reproduce the images. It also draws attention to a book Harvard sells for $40 with Renty’s portrait on the cover.
Among other demands, the suit asks Harvard to acknowledge it bears responsibility for the humiliation of Renty and Delia, and that Harvard “was complicit in perpetuating and justifying the institution of slavery.”
A researcher at a Harvard museum rediscovered the photos in storage in 1976. However, Lanier’s case argues Agassiz never legally owned the photos because he didn’t have his subjects’ consent, and he didn’t have the right to pass them on to Harvard. Instead, the suit says, Lanier is the rightful owner as Renty’s next of kin.
The suit also argues Harvard’s continued possession of the images violates the 13th Amendment, which abolished slavery.
“Renty is 169 years a slave by our calculation,” civil rights attorney Benjamin Crump, one of Lanier’s lawyers, said in an interview. “How long will it be before Harvard finally frees Renty?”
Lanier said she grew up hearing stories about Renty passed down from her mother. While enslaved in Columbia, South Carolina, the suit says, Renty taught himself to read and later held secret Bible readings on the plantation. He is described as “small in stature but towering in the minds of those who knew him.”
The suit says Lanier has verified her genealogical ties to Renty, whom she calls “Papa Renty.” She said he is her great-great-great-grandfather.
If given the photos, Lanier said she would tell “the true story of who Renty was.” However, she also hopes her case will spark a national discussion over race and history.
“This case is important because it will test the moral climate of this country, and force this country to reckon with its long history of racism,” Lanier said at a news conference outside the Harvard Club of New York City.